Light
Part 2 of 6
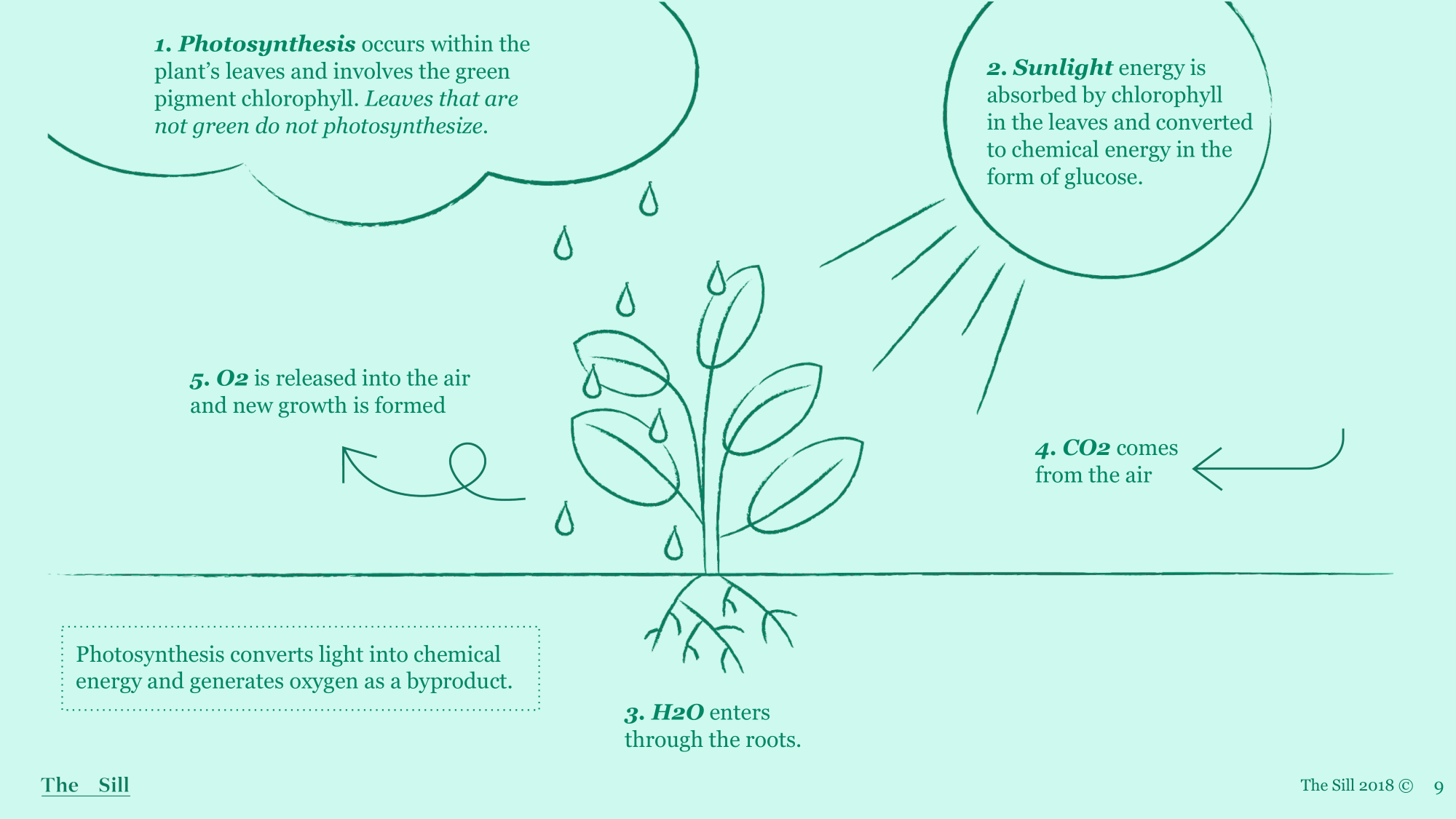
Photosynthesis
This is an overview of photosynthesis, look it over and think back to science class. Photosynthesis is the process used by plants to convert light energy into chemical energy that is later used to fuel different plant processes.
Plants need light from sun, CO2from the air, and water from the roots/soil in order to photosynthesize and they’ll release Oxygen as a byproduct.
Photosynthesis occurs at the leaves which is absorbed by the chlorophyll making the leaves the primary site of photosynthesis.
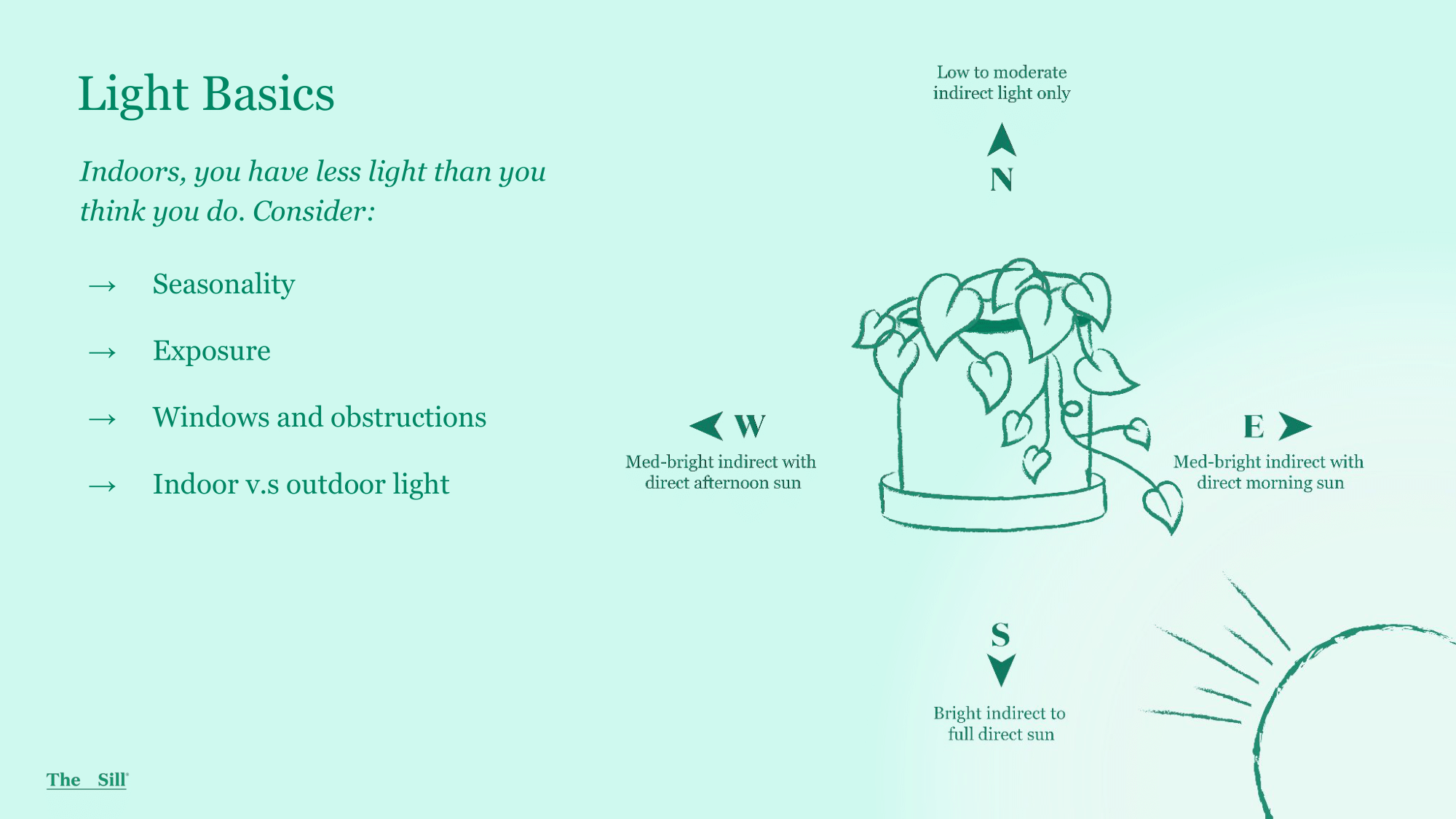
Light Basics
- Seasonality: Seasonality changes the directionality and angle of the sun (solstice/equinox). These seasonal changes can affect our plants growth.
- Spring & Summer are known as the growing season with the most daylight hours & active growth from plants.
- Fall & Winter are the dormancy phase where plants growth will slow down or cease. This is best to understand so you don’t need to worry about plants not actively growing in Fall/Winter where you’ll also see a decrease in the frequency of waterings compared to the growing season.
- Exposure: You can download and use a compass app on your smartphone to help determine your light level.
- North - Low to moderate indirect light only
- South - Bright indirect to full direct sun
- East - Med-bright indirect with direct morning sun
- West - Med-bright indirect with direct afternoon sun
- Windows: Smaller the window the closer the limit gets to how far away you can keep plants from the light source. Ideally, you should be placing plants directly in or no more than 2-3 feet from a window where it has a good view of the sky/outside. You can get away with placing plants farther if you have very large windows with no obstructions present, but ideally the closer to the light source the better for plants.
- Obstructions: Any obstruction blocking the plants view of the sky will diffuse the amount of light available for the plant to use. If window faces an alleyway, even if it’s South facing, it would be considered low light (example: trees outside window, etc.) Also keep in mind obstructions between the plant and its window (other large plants, decor, tv, etc.) which can also diffuse the amount of light available to a plant.
- Indoor vs Outdoor light: Some plant parents like to move their houseplants outdoors for the Spring/Summer months when conditions are most favorable. Outdoor light is much stronger so need to acclimate any plants that will be placed outside first. You can do so by placing plants in full/partial shade to start based on their light requirements and each week move them slowly into brighter light until they are in the ideal location.

Light Basics (Cont.)
- Direct vs Indirect sunlight: Remember light does not bend. If your plant is right next to or underneath a window the amount of light it receives will diminish considerably.
- Direct - The sun is in line of the plants “vision” to the sky.
- Indirect - Ambient light emitting from the sky but cannot see the sun.

Bright Light
Bright - Bright filtered/diffused light, a spot with direct sunbeams for more than 5 hours or completely diffused from direct sun.
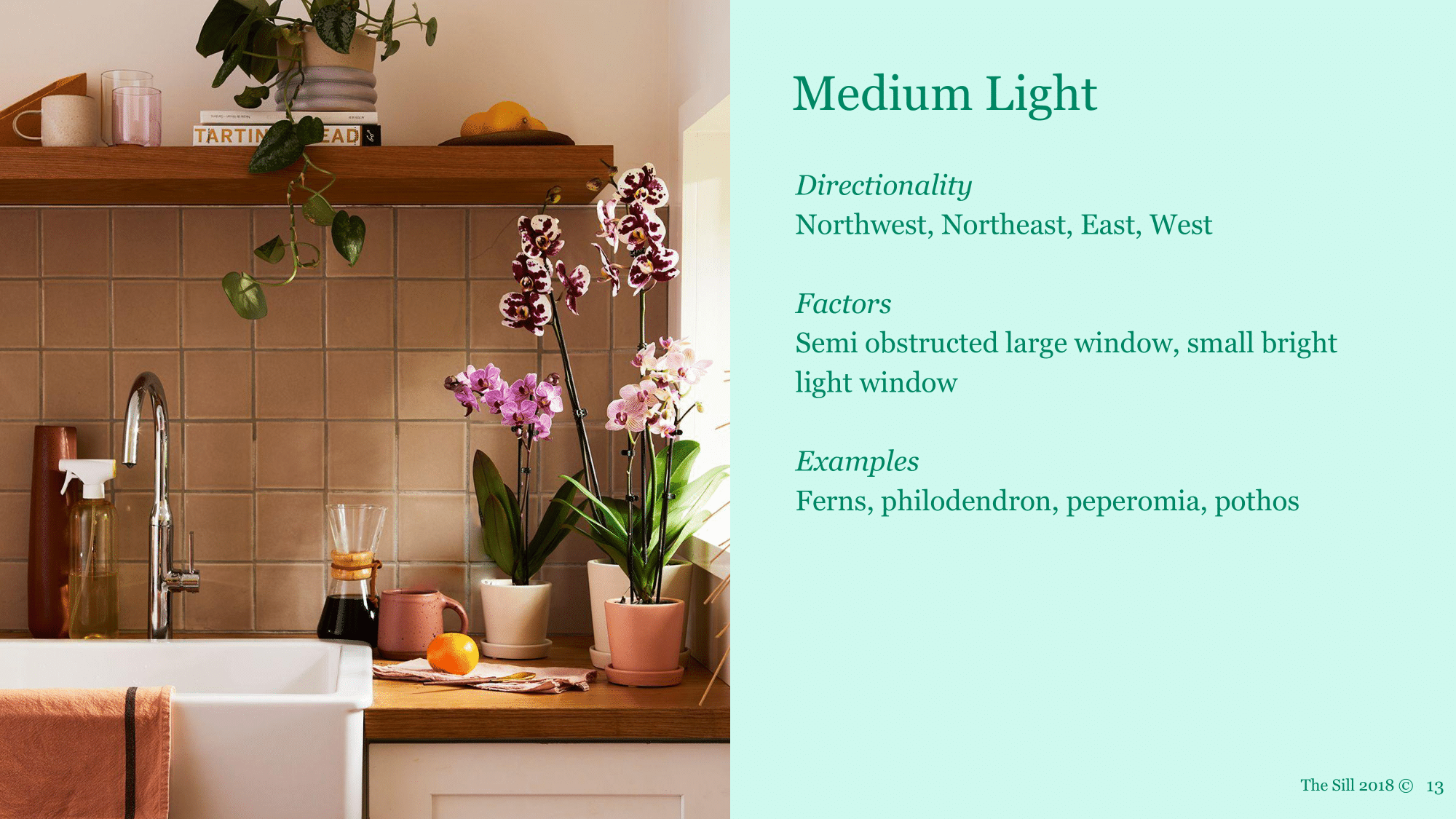
Medium Light
Medium indirect - filtered or diffused light, Medium light is a broad range. This can be a spot with some direct sun to indirect light in a window or more than 3 feet away from a bright window. Often apartments on the lower floors have medium to low light.
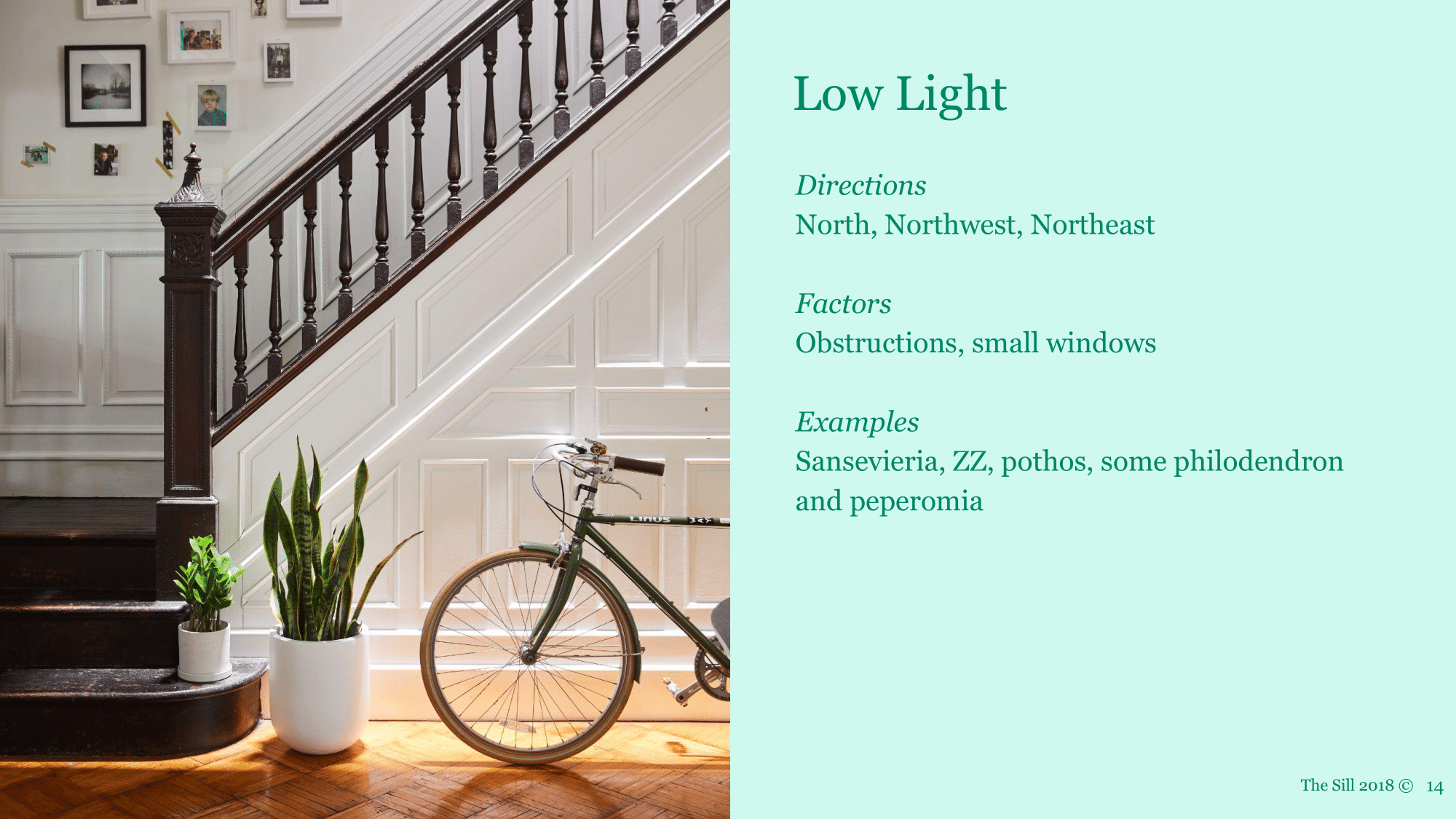
Low Light
Low light/low light tolerant - more than 4' from a window, or any space where the plant can see outside, but cannot see the sky.
- Low light plants tolerate low light but will always thrive better in brighter conditions. Place plants directly in low light windows to maximize sunlight. Consider incorporating artificial light.

Regulating Light
- Mirrors can help bounce ambient light overall in the home, and even aid low light plants in low light areas. However, not an effective way to boost light for bright light plants in lower light conditions.
- Sheer or gossamer curtains can help to diffuse strong light coming in during the Summer months for plants that may not like that intensity.
- Artificial light is supplemental light designed to stimulate plant growth. Regular light bulbs we buy for our lamps are not ideal for plant growth as the intensity is often weak and not in the right spectrum to most sufficiently drive photosynthesis. Recommend LED’s as the best.
- White walls helps to bounce off ambient light which can maximize light absorption for plants. Therefore, if you are moving or renovating and have a lot of plants consider white walls or backgrounds!
- Hanging plants - Plant parents can utilize things like wall/ceiling/macrame hangers, plant stands to elevate them off the floor so they are more in line with windows.
- Leaf/window cleaning -Cleaning leaves helps chlorophyll to be exposed to light in order to absorb it sufficiently. Can use white distilled vinegar or lemon juice diluted in water which helps to keep leaves shiny and remove mineral deposits. You can dry wipe just dust off with a microfiber towel. Neem oil can also work but would forgo using leaf shiners since they can be oily and clog the pores.
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Light
- 3. Environment
- 4. Watering
- 5. Potting & Drainage
- 6. Soil Mixes
